Azure serverless -- weather alert lab
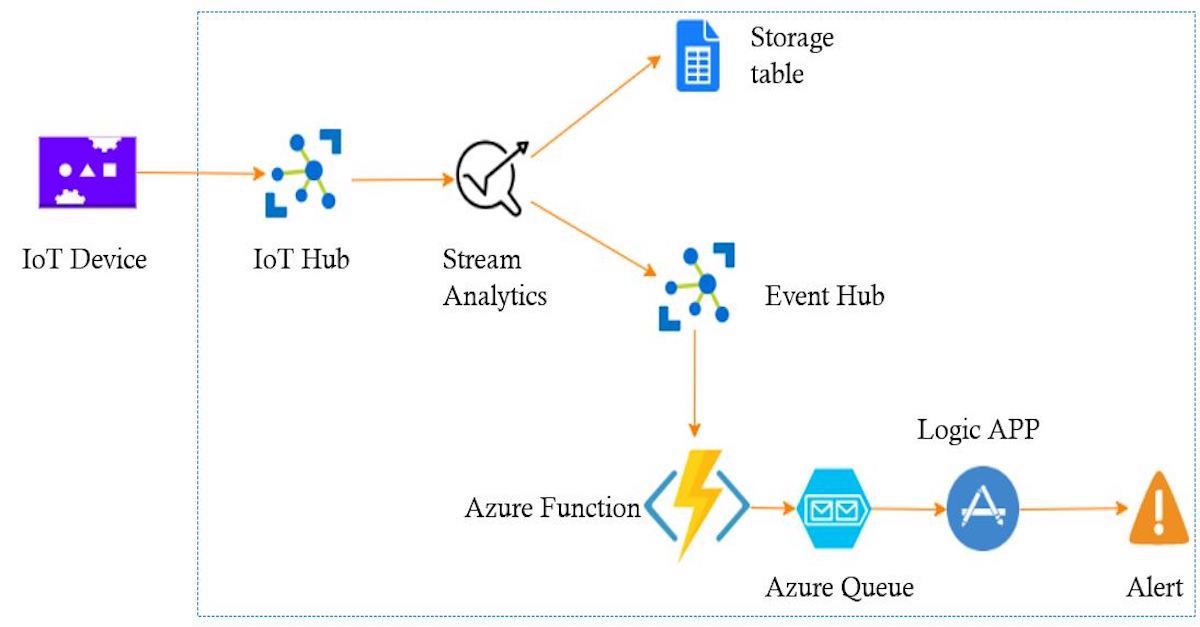
Azure Serverless components
Azure offers a variety of services that we can use to build application, one of the possibilities it offers is to create serverless application.
Serverless computing is the abstraction of servers, infrastructure, and operating systems.
Serverless is consumption-based, which means that you don’t need to anticipate any capacity.
Weather Alert Scenario
In this article I’m going to build weather alert system ,using a bunch of Azure Serverless component , the idea is to connect Azure environment to the IoT device , this device is going to send data to the cloud , and within the cloud environment I’m going to use Serverless components to manage, store and route data , at the end the system is going to send email alert when the temperature is greater than a given threshold
In this demo I’m using :
-
IoT Hub : To connect IoT device to Azure cloud environment
-
Azure Stream Analytics : To mange data in motion form the IoT hub
-
Storage Account :
Table : To store all data coming from the IoT device ‘cool storage’
Queue : to queue message alert before sending alerts
-
Event Hub : To connect different component within azure environment
-
Azure Function : serverless function will be in charge of getting data from the event hub and storing it in the Queue
-
LogicAPP : Get the alert from the queue and send emails alert
*NB : We are not obliged to use all of this components in our scenario , the idea is just to present the maximum of azure serverless components
In this article I’m using Azure Cli command with linux bash shell to provision Azure components*
I’m using Raspberry PI simulator to simulate an IoT device
IoT Hub
IoT Hub offers two way communication, from devices to Azure (D2C) and from Azure to devices (C2D), it can process millions of event per second and support multiple protocols such as MQTT, AMQP, MQTT over socket ,AMQP over socket, HTTPS, and file upload.
IoT Hub secures connection between the cloud and devices using device identity and shared access policies.
With the script below we create IoT hub , after that we create a device within the IoT hub, a resource group is created to contain all the components for this demo.
##Create a resource group
echo "Create resource group"
az group create --name $resource_group_name --location $location
## install Azure clit iot extenstion 'Should be done from azure cloud shell'
##az extension add --name azure-cli-iot-ext
##Create IOT hub and add device to the IOT HUB
echo "Create IOT Hub"
az iot hub create --name $iot_hub_name \
--resource-group $resource_group_name \
--location $location --sku $sku
##Create iot device
echo "Create a device to connect to the IOT hub"
az iot hub device-identity create --device-id $iot_device_name \
--hub-name $iot_hub_name \
--edge-enabled false \
--resource-group $resource_group_name
##Get device connection string
echo "Add IoT Hub Manage policy"
az iot hub policy create --hub-name $iot_hub_name \
--name $iot_hub_manage_policy \
--permissions RegistryWrite ServiceConnect DeviceConnect \
--resource-group $resource_group_name -o json
echo "Connection string to be used to connect your device to the IoT hub :"
az iot hub device-identity show-connection-string \
--device-id $iot_device_name \
--hub-name $iot_hub_name \
--resource-group $resource_group_name -o json \
--query connectionString
Once the IoT Hub and the IoT hub device are created , get the connection string from the last query to configure the device.
For this demo we are using Azure simulator, please change the connection string in the node JS code with your connection string, and click start.
The simulator start sending telemetry to the cloud ,if you check in your IoT Hub metric blade you will see telemetry coming to the cloud from your device
Storage Account
Azure offers variety type of storage account that can be used to store all sort of data in Azure (Blob storage, Table , Queue , File,disk)
For this demo , we create a storage account with a table storage , this table is going to be used as a cool storage to store all the data coming from the device.
With the script below we create a storage account and a table in the created storage account.
echo "Creating storage account"
az storage account create \
--name $weather_storage_account_name \
--resource-group $resource_group_name \
--access-tier Hot --sku Standard_LRS \
--location $location
echo "Creating Table in the created storage account"
az storage table create --name $weather_data \
--account-name $weather_storage_account_name
echo "Table Created"
echo "End of Creating storage account"
Event Hub
In the next step we are going to provision an Event hub, the main role of the event hub is to route data from different Azure component, in this demo an Event hub is going to route alerts from Azure Job Analytics to Azure function.
Event Hub is a messaging service available in Azure ,it is a fully managed, real-time data ingestion service , it can stream millions of events per second from any source to build dynamic data pipelines. within an event hub we can create consumer groups and it uses shared access policies to allow application to read or write in the event hub.
In this script we create event hub namespace , and then in the created namespace we add an event hub , the last two commands create two shared access keys , the first one to give write access to the events producer and the second one to give Read Access to the events consumer.
az eventhubs namespace create --name $event_Hubs_namespace \
--resource-group $resource_group_name \
--location $location \
--enable-auto-inflate true \
--maximum-throughput-units 20 \
--sku Standard
## Create an event hub. Specify a name for the event hub.
az eventhubs eventhub create --name $event_hub_name \
--resource-group $resource_group_name \
--namespace-name $event_Hubs_namespace
#create write and right access policies
az eventhubs namespace authorization-rule create \
--resource-group $resource_group_name \
--namespace-name $event_Hubs_namespace \
--name $sendauthorule \
--rights Send
az eventhubs namespace authorization-rule create \
--resource-group $resource_group_name \
--namespace-name $event_Hubs_namespace \
--name $readauthorule \
--rights Listen
Stream Analytic job
Azure stream analytics is high scalable service to Analyze data in motion, it supports SQL like query language for data analysis,it captures errors and connects services within an integration pipeline.
To develop Stream Analytic Job, we are going to use Visual Studio Code with Azure Stream Analytics extension.
To create a new project, add a new input file in Inputs Folder, I name this input IoTHub.json, this file contains parameters to connect to the IotIHub and process data in real time.
{
"Name": "IoTHub",
"Type": "Data Stream",
"DataSourceType": "IoT Hub",
"IoTHubProperties": {
"IotHubNamespace": "weather-alert-iot-hub",
"EndPoint": "messages/events",
"SharedAccessPolicyName": "iothubowner",
"SharedAccessPolicyKey": null,
"ConsumerGroupName": "$Default"
},
"DataSourceCredentialDomain": "c338ab22-0b90-44ae-a56a-8613b579c92e.StreamAnalystics",
"Serialization": {
"Type": "Json",
"Encoding": "UTF8",
"FieldDelimiter": null
},
"PartitionKey": null,
"CompressionType": "None",
"ScriptType": "Input"
}
You can test the connection and get a sample of data by using Preview data feature.
Now we add two outputs to the Stream analytic, the first one will be a storage account table, and the second one will an Event Hub.
{
"Name": "EventHub",
"DataSourceType": "Event Hub",
"EventHubProperties": {
"ServiceBusNamespace": "ns-weather-alert-event-eh",
"EventHubName": "weather-alert-event-eh",
"SharedAccessPolicyName": "readauthorule",
"SharedAccessPolicyKey": null,
"PartitionKey": "",
"PropertyColumns": []
},
"DataSourceCredentialDomain": "eb87e4ce-339e-40b6-9b48-d0307b3ff003.StreamAnalystics",
"Serialization": {
"Type": "Json",
"Encoding": "UTF8",
"FieldDelimiter": null,
"Format": "LineSeparated"
},
"ScriptType": "Output"
}
The last thing that we need, is to add queries to route data form the input to the outputs in *.asaql file
SELECT * INTO TableStorage FROM IoTHub
SELECT * INTO EventHub FROM IoTHub WHERE temperature > 29
The first query store all the data coming from the device to the storage table as a cool storage, the second query route data when temperature field has a value greater than 29.
You can test locally you job using local input data by using Run Locally feature, and compile the script using compile feature to generate the ARM template.
To deploy the job analytics, we use Azure Cli to deploy the generated ARM template.
iot_hub_manage_policy_sas=$(az iot hub policy list --hub-name $iot_hub_name \
--resource-group $resource_group_name \
--query "[?contains(keyName, 'manage')].primaryKey" -o tsv)
storage_account_key=$(az storage account keys list \
--account-name $weather_storage_account_name \
--query "[?contains(keyName, 'key1')].value" -o tsv)
eh_policy_send_primary_key=$(az eventhubs namespace authorization-rule keys list \
--resource-group $resource_group_name \
--namespace-name $event_Hubs_namespace \
--name $sendauthorule -o tsv --query primaryKey)
echo "Start executing ARM deployment to create ASA"
az deployment group create --resource-group $resource_group_name \
--name $deploymentName \
--template-file $template_file \
--parameters StreamAnalyticsJobName=$streamAnalyticsJobName \
Location=$location \
Input_WeatherAlertIoTHubInput_iotHubNamespace=$iot_hub_name \
Output_WeatherAlertEventhubOutput_serviceBusNamespace=$event_Hubs_namespace \
Output_WeatherAlertEventhubOutput_eventHubName=$event_hub_name \
Output_WeatherAlertEventhubOutput_sharedAccessPolicyName=$sendauthorule \
Output_WeatherAlertStorageTableOutput_accountName=$weather_storage_account_name \
Output_WeatherAlertStorageTableOutput_table=$weather_data \
Output_WeatherAlertStorageTableOutput_partitionKey=$deviceId \
Output_WeatherAlertStorageTableOutput_rowKey=$enqueuedTimeUtc \
Input_WeatherAlertIoTHubInput_sharedAccessPolicyName=$iot_hub_manage_policy \
Input_WeatherAlertIoTHubInput_sharedAccessPolicyKey=$iot_hub_manage_policy_sas \
Output_WeatherAlertEventhubOutput_sharedAccessPolicyKey=$eh_policy_send_primary_key \
Output_WeatherAlertStorageTableOutput_accountKey=$storage_account_key
Azure Function
Azure function is open source even driven serverless compute platform , we can run our code in serval languages with per use billing model and it integrates security.
As an even driven component, Azure Function supports by default serval triggers
- Triggers based on common scenarios
- HTTP request
- Scheduled timer
- Triggers based on Azure services
- Cosmos DB
- Blob and Queues
- Service Bus
- Event Hubs
- Trigger based on third-part services
- GitHub
- Twilio (SMS Messages)
We can create Azure Function using the portal, VS Code, Visual studio or any other IDE.
In our case, we create Azure function that has Event Hub as trigger, and Storage queue as output binding, the function will copy the data coming from the event hub to a Queue storage
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.Azure.EventHubs;
using Microsoft.Azure.WebJobs;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
namespace weatherAlertFunction
{
public static class Function1
{
[FunctionName("Function1")]
public static async Task Run([EventHubTrigger("weather-alert-event-eh", Connection = "EventHubConnectionString")] EventData[] events,
[Queue("Alert" , Connection ="weather_alert_storage_account")] IAsyncCollector<string> queue ,
ILogger log)
{
var exceptions = new List<Exception>();
foreach (EventData eventData in events)
{
try
{
string messageBody = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(eventData.Body.Array, eventData.Body.Offset, eventData.Body.Count);
await queue.AddAsync(messageBody);
// Replace these two lines with your processing logic.
log.LogInformation($"C# Event Hub trigger function processed a message: {messageBody}");
await Task.Yield();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
exceptions.Add(ex);
}
}
// Once processing of the batch is complete, if any messages in the batch failed processing throw an exception so that there is a record of the failure.
if (exceptions.Count > 1)
throw new AggregateException(exceptions);
if (exceptions.Count == 1)
throw exceptions.Single();
}
}
}
To deploy the function In azure environment we are going to use Azure Pipeline , first we need to push the function in to git repo, then provision Azure function compute in Azure and link the Azure function with the git repo.
When the function will be created, we are going to add parameters to connect the function with the Event Hub and Azure storage Queue.
storage_account_connection_string=$(az storage account show-connection-string \
--name $weather_storage_account_name --resource-group \
$resource_group_name --output tsv)
eh_policy_read_primary_connection_string=$(az eventhubs namespace authorization-rule keys list \
--resource-group $resource_group_name \
--namespace-name $event_Hubs_namespace
--name $readauthorule -o tsv --query primaryConnectionString)
az functionapp deployment source update-token --git-token $token
echo "Create the function app"
az functionapp create --resource-group $resource_group_name \
--name $weatheralertfunction \
--storage-account $weather_storage_account_name \
--runtime dotnet \
--functions-version 3 \
--consumption-plan-location $location \
--deployment-source-url $gitrepo \
--deployment-source-branch master
echo "Setup function settings"
az functionapp config appsettings set \
--resource-group $resource_group_name \
--name $weatheralertfunction \
--settings "weather_alert_storage_account=$storage_account_connection_string"
az functionapp config appsettings set \
--resource-group $resource_group_name \
--name $weatheralertfunction \
--settings "EventHubConnectionString=$eh_policy_read_primary_connection_string"
echo "Strat Fcuntion"
az functionapp start --resource-group $resource_group_name --name $weatheralertfunction
Logic App
Logic Apps is a serverless workflow offering from Azure. It has all the features of serverless technologies, such as consumption-based costing and unlimited scalability. Logic Apps helps us to build a workflow solution with ease using the Azure portal. It provides a drag and drop UI to create and configure the workflow.
In our case, we are going to create a logic App with three activities:
- Storage Account Activity: Get data from the queue
- Send Grid Activity : Send alert emails containing the data coming from the first activity
- Storage Account Activity: Delete message form the queue
You can create a logic App directly in the portal or you can use Visual Studio 2019 or VS Code , in my case I’m using Visual studio 2019 with the designer plugin , to create my Logic App.
Visual studio Create an ARM template to provision the Logic App ,you can use the script below to provision your Logic App
azurequeues_sharedkey=$(az storage account keys list \
--account-name $weather_storage_account_name \
--query "[?contains(keyName, 'key1')].value" -o tsv)
echo "Start executing ARM deployment to create LogicAPP"
az deployment group create --resource-group $resource_group_name \
--name $deploymentName \
--template-file $logicapp_template_file \
--parameters logicAppName=$logicAppName \
azurequeues_storageaccount=$weather_storage_account_name \
azurequeues_sharedkey=$azurequeues_sharedkey \
email_to=$email_to \
sendgrid_apiKey=$send_grid_api_key
Now you need just to start the temperature sensor and wait 2 or 3 minutes and you well get an email alert !!